This article contains affiliate links.
In recent years AI-driven literature-search platforms have sprung up like mushrooms after the rain, and they update at a dizzying pace. Beyond simple keyword search, many now offer citation-aware answers, automatic topic extraction and even “deep-research” modes that iterate with the user to produce richer reports.
This post (Part 1) surveys the major tools as of 2025, highlighting their core features and the latest upgrades.
If you'd like to learn more about how to tell these tools apart, check out the article below.
Three Core Features Found in Most Tools
- Citation-backed answers
The AI answers a question in prose and attaches numbered citations that link directly to the referenced papers. - Table-formatted summaries
Results can be reorganized into tables, making it easy to compare study designs, outcomes, sample sizes and so on. - Automatic topic extraction
The AI identifies key terms and topics related to the query and groups the retrieved papers under those topics.
Since late 2024 many platforms have also introduced so-called deep-research modes: the AI conducts additional rounds of analysis and writes an in-depth report instead of stopping at a single answer.
Part 1 below focuses on tools specialized in academic literature search. Part 2 covers services that can also handle general web content.
1. Consensus

Key Points
- Provides: Citation-backed answers
- Beginner-friendly, minimal interface (supports Japanese input and output)
- Each answer lists the cited papers with numbered links.
Why It’s Useful
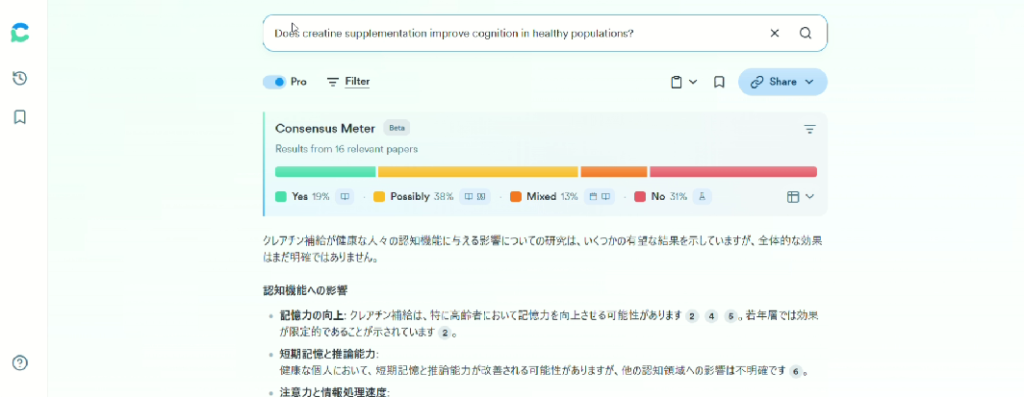
- Yes/No questions trigger a “Consensus Meter” that instantly shows the balance of supporting vs. opposing evidence.

- Icons indicate study type (observational, review, etc.) and citation count, so you can grasp quality at a glance.
- A Save button lets you bookmark interesting papers for later.
Caveats
The Consensus Meter is handy, but you still need to read the original papers to confirm the conclusions. Overall the tool is simple and ideal for first-time users of AI literature search.
2. Scispace

Key Points
- Provides:
- Citation-backed answers
- Table summaries
- Topic extraction
- One of the most feature-rich platforms (library management, writing assistance, reference formatting, etc.).
- Includes a Deep Review mode that refines your question through dialogue to produce a more detailed result.
Why It’s Useful
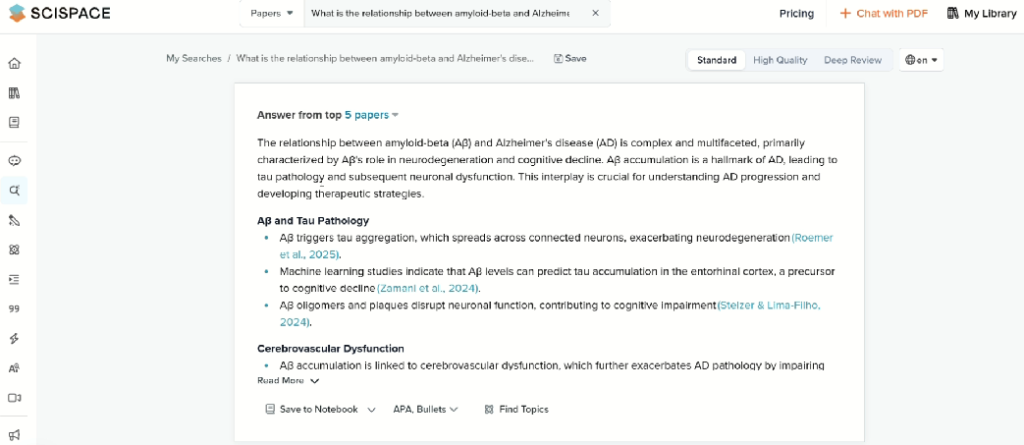
- Answers appear first; the reference list sits below.
- In table view you can add custom columns such as outcome or method.
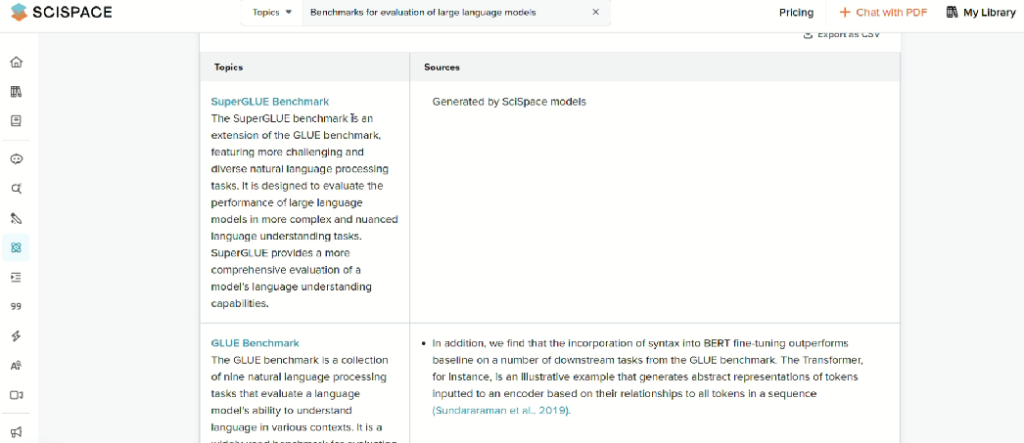
- Find Topics extracts key terms and shows which papers cover each term, again with citations.
Caveats
- The free plan limits search count and the number of cited references (e.g., five per query).
- Paid plans start at USD 12 / month for more queries and features.
- Translation quality has improved, yet occasional mistranslations remain; when in doubt use English.
3. Paperguide

Key Points
- Provides:
- Citation-backed answers
- Table summaries
- All-in-one platform similar to Scispace but with a cleaner interface.
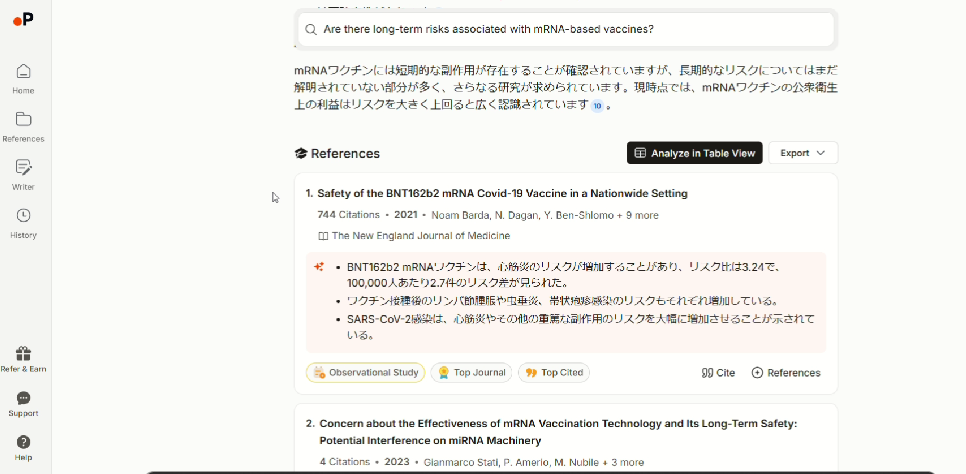
- Reference list shows helpful badges such as “Observational Study” or “Top Journal,” making it as intuitive as Consensus.
Why It’s Useful
- Enter a question; the answer and reference list appear immediately.
- Analyze in Table View converts results into a concise table.
- Good fit for users who want many functions but a simple layout.
Caveats
- Free tier limits the number of searches.
- Quality of auto-generated summaries and tables varies by paper.
- As with any tool, first test it on a topic you know well to gauge accuracy.
4. Elicit

Key Points
- Provides:
- Citation-backed answers
- Table summaries
- Topic extraction
- Delivers consistently high-quality search results despite a broad feature set.
- Get a Research Report (added late 2024) mimics a systematic review: it screens papers, applies explicit criteria and writes a structured report.
- English only.
Why It’s Useful
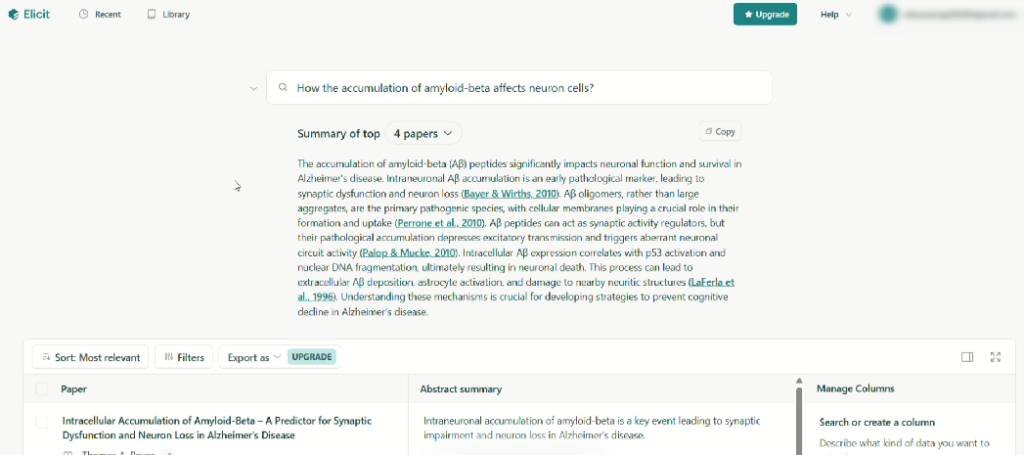
- Find Papers: shows a prose answer plus a customizable table—add “Methods,” “Outcomes,” etc.
- Topic extraction has long been one of Elicit’s strengths.

- Get a Research Report: though time-consuming, generates a meticulous systematic-review-style document, including screening flow and inclusion criteria.
Caveats
- Free plan limits the number of papers analyzed; paid plans (from USD 10 / month) allow hundreds.
- Because output is English-only, it can be challenging for non-English readers.
5. Scite

Key Points
- Provides: Citation-backed answers
- Specialized in citation relationships between papers.
- Tracks how other articles cite a given study (supporting, contrasting, or just mentioning).
Why It’s Useful
- Enter a query; the AI returns an answer with citations.

- For each citation Scite shows the exact sentence in the citing paper and which section it comes from.
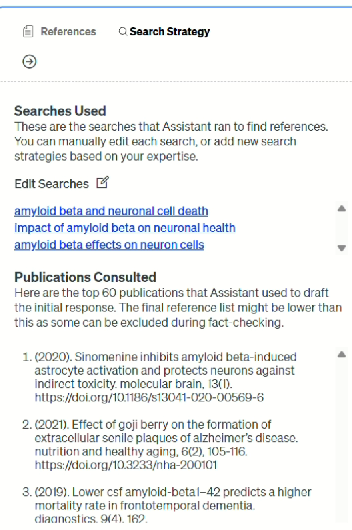
- Search Strategy lets you edit keywords and rerun the search—great for transparency and reproducibility.
- Upload your own paper to see how later studies have cited it (support, oppose, or neutral).
Caveats
- Emphasis is on visualizing citation networks rather than summary prose.
- Best suited to advanced users who need detailed citation context.
Tool-by-Tool Comparison
| Feature | Consensus | Scispace | Paperguide | Elicit | Scite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary purpose | Scholarly search | End-to-end: search, reading, writing | End-to-end: search, reading, writing | Scholarly search & summarization | Citation network analysis |
| Core search functions | Citation answers | Citation answersTablesTopics | Citation answersTables | Citation answersTablesTopics | Citation answers |
| Cheapest annual monthly price | $8.99 | $12 | $9 | $10 | – |
| Extras | – | Reading helper, library, writing assistant, video maker | Reading helper, library, writing assistant, adverb checker | High-precision search, systematic-review-like reports | Library; deep citation context |
| Deep-research mode | – | Deep Review | – | Research Report | – |
| Japanese support | Q&A both OK | Q&A & summaries OK | Q&A & summaries OK | Questions OK (answers in English) | Limited |
| UI complexity | Very simple | Many features, cluttered | Relatively simple | Many features, slightly busy | Citation-focused, data-dense |
Choosing the Right Tool
| Goal | Recommended Tool(s) |
|---|---|
| Quick, no-frills AI search | Consensus |
| Multi-purpose: writing, library, management | Scispace or Paperguide |
| Maximum coverage & depth | Elicit (plus Scispace Deep Review) |
| Detailed citation context (pro/contra mentions) | Scite |
Tool strengths and search precision differ widely. During early exploratory reading, Consensus, Scispace or Paperguide may suffice. When drafting a manuscript you’ll likely need broader coverage—Elicit or Scite, and perhaps a network tool like Research Rabbit for even greater recall.
Regardless of platform, AI summaries can omit or misinterpret details. Always check the original papers before you draw final conclusions.









コメント